Introduction
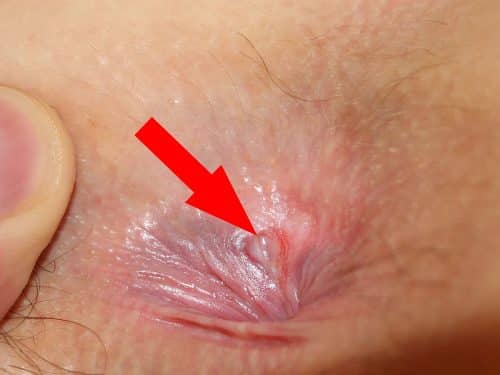
An anal fissure is a tear in the mucosal lining of the anal canal, most commonly due to trauma from defecation of hard stool. It can be classified according to its duration:
- Acute – present for <6 weeks
- Chronic – present for >6 weeks
Anal fissures can also be categorised by whether they are primary (no underlying disease) or secondary (underlying disease e.g inflammatory bowel disease).
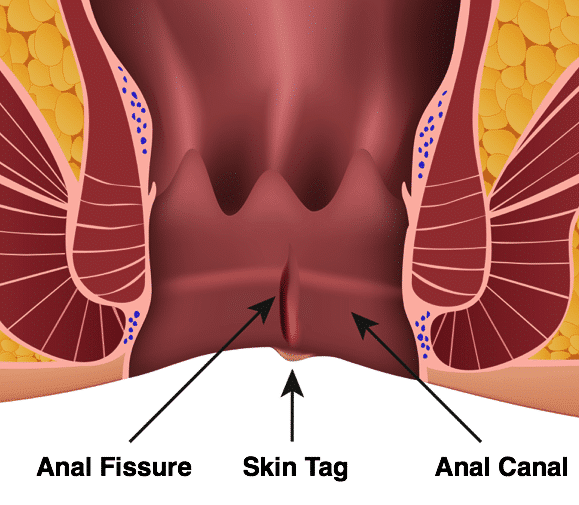
Figure 1 – Illustration of an Anal Fissure, with associated skin tag
Risk Factors
Anal fissures are usually caused by inflammation or trauma to the anal canal. The major risk factors include constipation, dehydration, or inflammatory bowel disease.
Clinical Features
The most common presenting feature of an anal fissure is intense pain post-defecation, which can last several hours. Pain can be far out of proportion to the size of the fissure. Other associated symptoms may include bleeding (commonly bright red blood on wiping) or itching, both typically post-defecation.
On examination, fissures can be visible and / or palpable (albeit very painfully) on digital rectal examination (Fig. 2). Most fissures present in the posterior midline (90% cases); anterior fissures are more likely to in females (especially after childbirth) or if an underlying cause is present*.
Often patients will refuse a digital rectal examination due to the intense pain and examination under anaesthesia (EUA) may be necessary for diagnosis. Fissures within the anal canal can then usually be identified upon proctoscopy.
The differential diagnoses include haemorrhoids, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, or anal cancer.
*Multiple fissures or anteriorly located fissures are more likely to be due to an underlying cause and require further investigations (if no known cause is apparent)
Management
Medical Management
The medical management of an anal fissure involves treating any underlying precipitating factors and providing adequate analgesia. The majority of patients do not require surgery.
Advise the patient to increase their fibre and fluid intake and can trial stool-softening laxatives (such as Movicol) if needed. Topical anaesthetics, such as lidocaine, can also provide short term symptomatic relief.
In symptomatic patients, GTN cream or diltiazem cream can be trialled – these act by increasing the blood supply to the region and relaxing the internal anal sphincter, putting less pressure on the fissure, promoting healing, and reducing pain.
Surgical Management
Surgical therapy is mainly reserved for chronic fissures, where medical management has failed to resolve the symptoms.
Most patients will be trialed initially with Botox injections, given into the internal anal sphincter acting to relax the sphincter and promote healing of the fissure.
In patients with ongoing symptoms despite these measures, a lateral sphincterotomy can be performed (Fig. 3), involving division of the internal anal sphincter muscle.
Recurrence of anal fissures post-surgery occurs approximately in 1-5% patients.
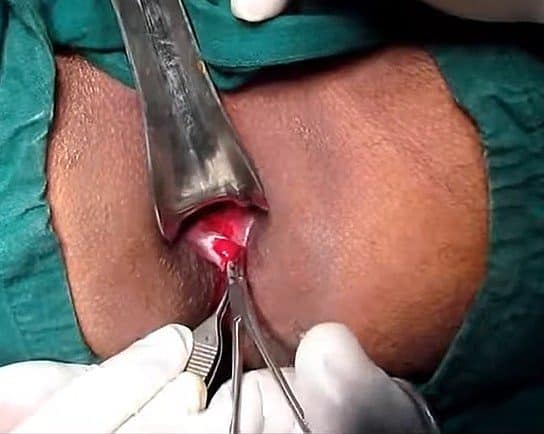
Figure 3 – A Lateral Sphincterotomy being performed, to treat a patient with a chronic anal fissure
Key Points
- Anal fissures present with intense pain post-defecation, as well as potential bleeding or itching
- Risk factors include constipation and IBD
- Most cases can be managed conservatively with medical management
- Consider investigating for underlying causes for those with anterior fissures or recurrent disease